Digitalization can contribute to the economic growth of developing countries, particularly by promoting private sector development and financial inclusion.
The articles in this category allow the audience to have a better understanding of different topics related to African entrepreneurship: the economic or political context, social issues, etc.
Faced with school closures in at least 188 countries around the world as a result of the Covid-19 crisis, many educational institutions have had to set up a distance learning…
Faced with school closures in at least 188 countries around the world as a result of the Covid-19 crisis, many educational institutions have had to set up a distance learning system. This temporary reorganization of activity will certainly have a strong and lasting impact on educational structures.
If this distance learning is sometimes complex, particularly because of the problems of connection or availability of computer tools, it is even more so for the early childhood sector, given the risk of overexposure of toddlers to digital tools and the lack of autonomy of the latter in their learning, as evidenced by the three actors dedicated to this sector met for this article.
Reinventing learning
The current health crisis has forced educational institutions as a whole to reinvent and rethink their activities. La Coccinelle, a network of crèches and nursery schools in Côte d’Ivoire, has put online exercises, educational games, nursery rhymes and some graphic design, pre-reading and mathematics activities so that children do not lose their skills. At Kër ImagiNation, a learning and cultural center for children in Senegal, online sessions by Zoom were carried out in small groups to enable better participation by the children. As the sessions progressed, the content and the way of interacting with the children at a distance became more refined, for example by using puppets or proposing simple educational experiences, such as an experiment on water, which the children could carry out at home with their parents.
E-learning, although possible and sometimes even favorable for theoretical subjects, does not easily lend itself to practical learning. At La Coccinelle, for example, parents had to print out the exercises to enable the children to work on paper. Because many fields, such as graphic design, cannot be learned online. At the Institut Académique des Bébés in Senegal, a training school dedicated to the professional training of children’s professions, practical subjects represent about 45% of the learners’ curriculum. For these subjects, e-learning was not feasible and practical workshops were conducted on the premises, in small groups. However, this required a significant investment for the promoter, as the whole school organization had to be rethought. The space had to be rearranged in order to respect the meter of social distance between the learners. Masks and hydro-alcoholic gel had to be purchased to equip the learners and trainers. Finally, between each group, the premises had to be disinfected.
E-learning, although possible and sometimes even favorable for theoretical subjects, does not easily lend itself to practical learning.
Many difficulties arise with this learning
The crisis revealed huge disparities in the level of emergency preparedness of countries, children’s access to the Internet and the availability of educational materials. These difficulties make it difficult for children who are far away from these tools to learn. In addition, distance learning has often required the training of both parents and trainers in digital tools.
Finally, home-schooling for toddlers requires the presence of a parent or an adult who is able to accompany the child in his or her learning. However, the latter’s professional occupations were not necessarily compatible with the children’s needs. The closure of schools left parents confused about how to support their children’s learning at home. Aware of these issues, Karima Grant, founder of Kër ImagiNation, now wishes to develop a project specifically dedicated to parents, in order to support them, through a platform, in parenting and pedagogy.
The same concern: the future of the early childhood sector and, consequently, the future of these children
The realities of the early childhood sector are of particular concern, as the recovery of tuition fees is even more complex in times of school closures, compounded by the costs of school staff and operations. Many early childhood actors in Sub-Saharan Africa are today in a delicate situation, with an uncertain start to the new school year.
The latter feel forgotten by the public authorities, even though the early childhood sector is essential for the development and construction of the child. In Bangladesh, a study implemented by the World Bank’s Strategic Impact Evaluation Fund (SIEF) revealed that providing young children with an extra year of pre-school education is an effective way to improve school readiness for both boys and girls (especially girls). Researchers measured the impact of an extra year of preschool for children at age 4, compared to the standard year of only one year from age 5. After two years, children who were offered an extra year of preschool had significantly higher scores in literacy, numeracy and social-emotional development than children who were offered preschool only from age 5.
According to Sara Adico, director of La Coccinelle, “The awakening, simulation and development of children have been left behind. But if early childhood is well supervised, it promotes a good psychological development of the child, which is beneficial for the whole nation”.
Children have already begun to unlearn, both in terms of skills (graphics, dictation, etc.) and psychic skills (social interactions, motor skills, etc.), a situation that is more serious for children with psychosocial problems. According to these actors, if the situation were to drag on, it should affect primary, secondary and finally higher education in the years to come, and thus represent a real problem in term of human capital and economic repercussions.
If the situation were to drag on, it should affect primary, secondary and finally higher education in the years to come, and thus represent a real problem in term of human capital
Whether for Sara Adico of La Coccinelle, Karima Grant of Kër ImagiNation or Fa Diallo of IAB, the current crisis can be an opportunity to reinvent and rethink the early childhood sector. It is a way for the early childhood education community, once the weaknesses of the digital tool as a solution to early childhood distance learning are recognized, to seek innovative solutions to improve the added value of child care. But for this to happen, a reflection must be conducted with all stakeholders (families, public institutions, major employers, etc.) to find and create systems that are conducive to the psychological development of children. With regard to early childhood, it is not appropriate to limit efforts in the field of health or nutrition, since the lack of quality early childhood care structures can be especially damaging to the child’s psychological development and thus, in the longer term, have real economic and human capital implications.
Read more
![]() Discover the article “African schools: facing the covid-19 crisis”
Discover the article “African schools: facing the covid-19 crisis”
Today, many young girls face significant barriers in accessing education (primary, secondary and higher education), in obtaining decent and remunerative employment, in accessing finance, etc. Their education is often considered…
Today, many young girls face significant barriers in accessing education (primary, secondary and higher education), in obtaining decent and remunerative employment, in accessing finance, etc. Their education is often considered a low priority, when in fact it is a first step towards their emancipation and empowerment.
Inclusive, relevant and quality training…
Sub-Saharan Africa has 30 million children excluded from the school system. Girls, rural populations and marginalized communities are particularly affected. One of the most persistent obstacles to girls’ schooling is the low value placed by society on their education. When schooling is no longer compulsory, families do not enroll their daughters, not only for financial reasons but also because of social norms (keeping girls at home, early marriage and maternity, inadequate school infrastructure, discrimination, etc.).
Primary education has received significant support from Governments and development aid, which has led to considerable progress. In Sub-Saharan Africa, 34% of countries had achieved gender parity in primary education by 2017. This performance falls to 21% for lower secondary, 5% for upper secondary and 0% for tertiary education[1]. Due to a lack of sufficient financial and human resources, higher education has received less attention, even though the needs are immense and gender inequalities blatant.
To become true actors in the development of their region and their country, girls and young women need continued access to relevant and quality education. Second-chance’ programs for vulnerable women and young women who have not received sufficient education to enable their empowerment may be considered. UNWomen is developing its Second Chance Education and Vocational Learning (SCE) program to provide a comprehensive solution for marginalized women and young women who have missed out on education and who are at risk of being left behind. This project aims to develop context specific, affordable and scalable learning, entrepreneurship and employment pathways for empowering the world’s most disadvantaged women and young women.
It is also a question of changing mentalities, for example by developing gender-neutral educational content and setting up awareness-raising activities designed to change the perception that both men and women may have of the career prospects open to young women.
… enables access to economic opportunities …
Significant differences between men and women have emerged in the labor market, according to sector of activity; occupation and type of employment (vertical and horizontal gender segregation). Women frequently work in sectors where they are less likely to benefit from training that could lead to career development or a change of occupation. Africa is the second least egalitarian region in the world in terms of women’s participation in the formal economy. Nearly 90% of employed women on the continent work in the informal economy, compared to 83% of men[2].
Women’s participation in the world of work and their professional advancement also face considerable obstacles that are the result of sectoral and organizational cultures and practices dominated by values, beliefs and patterns of behavior (encouraged or reinforced by social norms and institutions).
Women are thus less likely than men to study science, technology, engineering and mathematics. In 2013, the share of women graduates in science and engineering was 19% and 21% respectively in Burkina Faso and 27% and 18% in Ghana[3]. Lack of information on opportunities in these male-dominated sectors, psychosocial factors, lack of role models, networks and biased gender norms are some of the factors that explain these dynamics.
In addition to traditional skills such as literacy and numeracy, digital skills have long since become one of the key areas of expertise for the 21st century. 55% of women entrepreneurs say that improving their technical expertise is a priority. However, nearly one billion girls worldwide (65% of all girls and young women under the age of 24) do not possess these skills, that are essential to participate in the world of work in the future. Some players have already positioned themselves on this issue. This is the case, for example, of the Ghana Code Club[4] that, with its “Code on Wheels” project, will organize a mobile coding workshop for girls and women aged 12-24 in different regions of the country. The workshops provide participants with a fun and practical introduction to computer thinking and technical skills.
… in favor of the economic and social emancipation of women.
These economic opportunities then play a central role in social relations and enable women to assert themselves as members of the economic society, which is a first step towards empowerment and emancipation.
Giving more women access to economic opportunities, entrepreneurship, free consumption and the chance of being an integral part of economic life not only significantly reduces gender inequalities, but also transforms society and the economy as a whole. Indeed, gender inequality hinders economic and social development. It is estimated to cost sub-Saharan Africa an average of US$95 billion a year, peaking at US$105 billion in 2014 – or 6% of the region’s GDP –[5] which undermines the continent’s efforts for inclusive human development and economic growth.
Access to quality education, especially for girls, is thus essential to combat the cycle of poverty and to ensure a more inclusive society with equal opportunities for all.
Resources
[1] Rapport mondial de suivi sur l’éducation 2019: Migration, déplacement et éducation: bâtir des ponts, pas des murs, UNESCO, 2019
[2] The power of parity: Advancing women’s equality in Africa, McKinsey Global Institute, November 2019
[3] Is the gender gap narrowing in science and engineering, Unesco, 2015
[4] Pour en savoir plus sur le Ghana Code Club
[5] Rapport sur le développement humain en Afrique 2016 : Accélérer les progrès en faveur de l’égalité des genres et de l’autonomisation des femmes en Afrique, PNUD, 2016
The management of the Covid-19 pandemic is disrupting global education. The closure of schools and universities across 184 countries have sent home 1.5 billion students, representing more than 90% of…
The management of the Covid-19 pandemic is disrupting global education. The closure of schools and universities across 184 countries have sent home 1.5 billion students, representing more than 90% of the world’s students [1].
Since mid-March, a large proportion of African schools and universities have closed their doors. However, these closures do not mean that teaching activities have come to a complete cessation. Whether public, private or supported by associations, all institutions are trying to do their best to provide transitional solutions so that pupils can continue their schooling and so that the precious learning time is not lost for good.
The group Investisseurs & Partenaires, which supports some fifteen companies in the education sector, can testify the strong resilience and innovative spirit of these actors. From nurseries to high schools and training centers, these companies are showing that they can adapt their business during a crisis that is hitting them hard. This article is largely based on I&P’s portfolio, but also includes some other noteworthy initiatives.
E-learning: an obvious choice?
In order to ensure continuity of teaching activities, many institutions rely on e-learning systems. This is for example the case of Enko Education’s network of high schools, whose courses have been taking place since the end of March on a new online platform. Following the creation of a crisis committee, new working methods have also been introduced. Teachers must now ensure that each student has daily access to the resources needed to follow the courses, either in digital format or by printing the booklets sent to the families[2]. In the early childhood sector, where screen time must be limited, it is the relationship between parents and pre-school structures that needs to be reinvented. Thanks to social networks, newsletter, WhatsApp groups and other communication media, specialist companies, such as Ker Imagination in Senegal [3], can support parents to promote good practice at home and strengthen the learning community.
Some educational companies made distance learning the core of their model long before the crisis. The startup Etudesk, based in Abidjan and supported by Comoé Capital, has thus developed valuable expertise in building tailor-made e-learning platforms with various partners. Today, Etudesk supports about ten educational institutions in Ivory Coast and Senegal to adapt and put online their pedagogical content in the best possible time and conditions. African Management Institute builds distance and face-to-face training courses for entrepreneurs and SMEs in East Africa. AMI currently provides a free “survival kit” to entrepreneurs to learn crisis management and make the right decisions in the face of serious risks to their business [4]. Another exciting example is the Mali-based company Kabakoo, which is exploring a new model of engineering training that focuses on “solutions to concrete and immediate problems” in its environment. Kabakoo is now making its international platform available for its learners and experts to design and manufacture objects useful in the fight against Coronavirus, such as artificial respirators and masks [5]. With a unique positioning in the technology and education sector, Etudesk, AMI and Kabakoo are leveraging their capacities for innovation and resilience to bring rapid and concrete responses to traditional educational players as well as to companies and citizens.
With a unique positioning in the technology and education sector, these companies are leveraging their capacities for innovation and resilience to bring rapid and concrete responses to traditional educational player
Connectivity, cost and learning conditions: the challenges of home schooling
However, the good practices that are emerging here and there face many difficulties. In West Africa, household connectivity is not provided in large rural or isolated areas [6]. In addition to the challenges of Internet coverage, there is also the issue of the cost involved for consulting these tools online. Other channels are thus necessary and several initiatives are underway to improve the inclusion of education systems in the time of the coronavirus and to limit the risks of school dropout [7]. National radio stations and television channels can be massive solutions for disseminating educational content [8], provided that there is enhanced cooperation between the ministries concerned and the telecom company, as it is the case in Ivory Coast [9].
On the other hand, it will be necessary to ensure that pupils can study under good conditions and with assiduity, which is in fact the major issue on which e-learning offers little information for the moment. A fundamental reflection on the role of teachers and on distance teaching methods must be carried out to accompany the development of educational technologies.
Economic impacts are immediate and lasting
Finally, the coronavirus crisis poses a very strong threat to the financial sustainability of companies in this sector. With a complete revenue freeze that could last until September, educational companies must seek to maintain a good relationship with all their stakeholders, especially their employees. Specific measures can be envisaged in the short term, such as adjusting cash flow plans, eliminating non-essential charges, prioritizing creditors, etc. For the most robust institutions, these measures will undoubtedly be sufficient and will probably be in addition to the benevolent support of banking partners. But for a majority of the more vulnerable private players, additional and significant support measures will be absolutely necessary for their survival. Governments, donors, investors and all education financers will have to provide appropriate responses as quickly as possible.
The opportunity to transform education
The current experience is unprecedented. The educational enterprises best prepared for the crisis were those that had integrated, even if incompletely, the challenge of digital transformation into their model. Thus, the coronavirus crisis provides the entire education sector with perhaps an unprecedented opportunity to deploy new models that resonate with the aspirations and practices of new generations of learners.
Broadening access to content, opening up populations, developing new services, individualizing educational pathways, building new learning communities: the potential of digital education is considerable, both for the company and for its beneficiaries. After today’s emergency, it will undoubtedly be time for all those involved in the education sector to re-imagine their model while keeping the issues of accessibility, inclusion and quality at the heart of their principles.
The current crisis provides the entire education sector with an unprecedented opportunity to deploy new models that resonate with the aspirations and practices of new generations of learners.
Notes
[1] Informations de l’UNESCO au 7 avril 2020 https://en.unesco.org/news/unesco-launches-codethecurve-hackathon-develop-digital-solutions-response-covid-19
[2] https://enkoeducation.com/fr_FR/covid-19-and-school-closings-enko-education-implements-distance-learning-in-all-its-schools-across-africa/
[3] https://www.facebook.com/KerImagiNation/
[4] https://www.africanmanagers.org/all/news/keep-thriving-ami-learning-covid-19/
[5] https://www.kabakoo.africa/blog/une-bonne-vieille-machine-a-coudre-et-du-fil-contre-covid-19
[6] Voir par exemple l’indice de connectivité développé par GMSA montrant les déficits d’infrastructure et de connectivité dans la zone Afrique de l’Ouest https://www.mobileconnectivityindex.com/#year=2018
[7] Voir les risques soulignés par Jeune Afrique au Sénégal : https://www.jeuneafrique.com/922593/societe/senegal-les-bons-et-les-mauvais-points-de-lecole-a-distance-au-temps-du-coronavirus/
[8] Voici les différents canaux d’enseignement à distance recensés par le GPE : https://www.globalpartnership.org/blog/school-interrupted-4-options-distance-education-continue-teaching-during-covid-19#.XoXPayoKbqI.linkedin
[9] Voir ici l’initiative du gouvernement ivoirien qui a démarré le 6 avril 2020 pour les classes d’examens (CM2, 3ème, Terminal). http://www.gouv.ci/_actualite-article.php?recordID=11002
It is hard to predict the unpredictable, especially when it is unknown. However, that is what the leaders of all countries must try to do at this time.
It is hard to predict the unpredictable, especially when it is unknown. However, that is what the leaders of all countries must try to do at this time.
This post is a plea for Mauritius to join the ACCTS negotiations.
Promoting employment is one of the priorities of the African continent for the coming years. According to the African Development Bank, only 3 million formal jobs are created each year…
Promoting employment is one of the priorities of the African continent for the coming years. According to the African Development Bank, only 3 million formal jobs are created each year in Africa, while 10 to 12 million young people enter the job market.
In 2019, Algeria has been at the forefront of African political life, with the resignation of President Abdelaziz Bouteflika in April. The economy is currently suffering, not so much from…
In 2019, Algeria has been at the forefront of African political life, with the resignation of President Abdelaziz Bouteflika in April. The economy is currently suffering, not so much from its growth rate, price, and cost competitiveness, as from its inability to diversify and create the hundreds of thousands of jobs needed each year for the annual cohort of young people who enter the labor market.
A lack of public support for entrepreneurship
When we compare its political and economic governance to other countries, Algeria is lagging behind the North African average, and in some aspects, behind the African continental average.
The Algerian context of individual freedoms has not allowed citizens to engage in politics fully. In this background, the accountability of public decision-makers has been structurally low, although raw material resource rents have helped to buy some “social peace” through subsidies for household consumption (Le Billon, 2003).
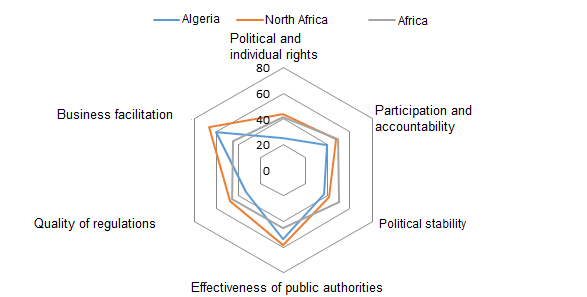
The last four presidential terms (1999-2014) have permitted a return to civil peace. The regime has gradually opened up to more cooperation with the private sector, but has never really abolished cronyism. Consultation frameworks have fostered actors close to, and respectful of, the authorities. This networking spirit has produced significant shortcomings in the transparency of public actions and the establishment of effective competition mechanisms. With an inexorable rise in social discontent, the government’s responses focus more on the short term than on the implementation of a strategic vision with long-term measures compatible with the requirements of globalization and job creation.
The continuation of half-measures has helped to alter the desire for reforms to protect the economy from the vulnerabilities associated with the downturn in the commodity “super cycle”. Short-term rent management and cronyism have hindered the initiative of local entrepreneurship and have not taken into account long-term perspectives in a context of high corruption.
So far, both the stimulation of business creation and the opening of tenders to agents without connections to the “political clan” have remained timid. Current events will determine to what extent the organization of political, economic, and social life will lead to public order and civil peace. The success of the change of President will determine Algeria’s ability to project itself into the more integrated sub-regional space which is expected to develop with the prospect of ECOWAS enlargement and the establishment of the African continental free trade area.
Prices and costs in line with competitiveness
The FERDI Sustainable Competitiveness Observatory (SCO) has Algeria in first place to for price competitiveness, both for North Africa and for the whole continent. This position, which could not be more flattering, cannot fail to amaze. It suggests that diversification has not suffered from the “Dutch disease” caused by oil and gas rents, which generally drives up costs to the point of crowding out the production of non-primary tradable goods (Djoufelkit 2008).
The purchasing power conversion factor against the dollar estimates that the cost of the basket of goods in 2016 was only 25% of the price in the United States, 40% of the African average and 30% of the average for North African countries (Graph 1). In Algeria, the level of wages is also relatively low. The wages of a cashier in a supermarket are much lower, at the current exchange rate than in other North African countries, and are not very far from the African average; but Algeria is an upper-middle-income country. However, a more detailed analysis of prices leads to nuanced conclusions.
Graph 1: Evolution of the Algerian Dinar conversion factor
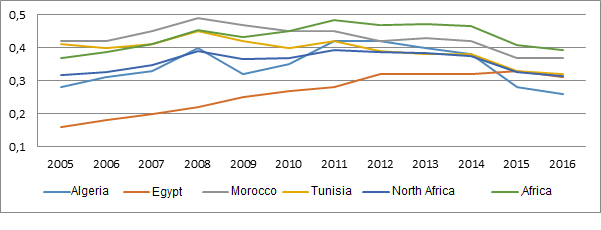
* The conversion factor for purchasing power parity used here is the number of units of national currency required to purchase the same amount of goods and services in the domestic market that a US dollar would buy in the United States.
The first reason for the nuanced price competitiveness is the consequence of an interventionist tradition which contributes to define prices that do not necessarily reflect the reality of market prices, and to a framework of commercial margins that is still prevalent. In December 2017, a problem arose in concrete terms for bread. Hundreds of bakeries had taken the initiative to defy public regulations by raising the price of a baguette to 15 dinars. At that time the official price was 8.5 dinars, unchanged since 1996, with a typical price of 10 dinars in Algiers. According to the federation of bakers, which is not recognized by the Government, the price regulation, which no longer covered production costs, could force many bakeries to close. The difficulty is to make economic logic and social logic compatible. As in most developing countries, the price of bread is a sensitive issue, because it is an essential part of household food consumption. For a population of more than 41 million inhabitants in 2017, 70 million baguettes would be sold every day!
Interventionism in price may correspond to instant consumer protection, but may cause problems in the longer term. It impoverishes the competitive market and leads to the emergence of cheating on product quality. Beyond bread, public preference for regulation can, therefore, lead to distortions in the allocation of resources within the economy. It leads to uncertainties about the profitability of companies with implications that are poorly measured for the long-term well-being of the community
The second reason for the nuanced price competitiveness, stems from public subsidies. With prices maintained below the economic cost, a subsidy can compensate the producer for the loss of income. For this economic logic to hold permanently, it is necessary to assume that these subsidies are sustainable. To validate this assumption information about the cost of oil and gas production is strategic. However, little is known about it. For Algeria, the break-even point per barrel of oil would be a price of between $20 and $40. Given the importance of oil and gas in the country’s economy, we can see the influence of these rents on GDP and their contribution to the financing of the State budget (upto 60% of revenue).
Graph 2: The percentage of rents in Algeria’s GDP (1990-2016)
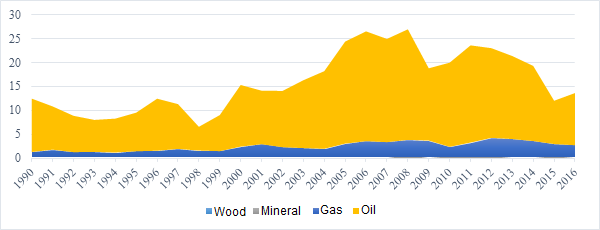
Consumer subsidies and transfers to the economy have become the Achilles’ heel of Algerian public finances. Their share of GDP has tended to increase since the late 1990s, from 4% to around 12% in 2012, while in 2012 oil prices had not yet started to decline. The consumer products concerned are numerous. In the fiscal year 2015, IMF staff estimated that subsidies cost about 14% of GDP and were equivalent to twice the combined annual budgets of the Ministries of Health and Education. According to the most recent figures from the Ministry of Finance, about 10% of direct subsidies are covered by the State budget. 18% are implicit subsidies, such as tax advantages granted to companies for their investments, which are more difficult to assess,. The role of these subsidies is essential. Probably, the new Algerian government team will quickly be faced with the daunting dilemma of choosing between companies and consumers, between the short term and the long term in an approach that has to be both coherent and compatible with political feasibility.
References
Le Billon, P. (2003). Buying peace or fuelling war: the role of corruption in armed conflicts. Journal of International Development, 15(4), 413-426. https://doi.org/10.1002/jid.993
Djoufelkit. H, (2008), « Rente, développement du secteur productif et croissance en Algérie », AFD, Document de travail, n°64, Paris. https://www.afd.fr/
Observatoire de la compétitivité durable : https://competitivite.ferdi.fr/