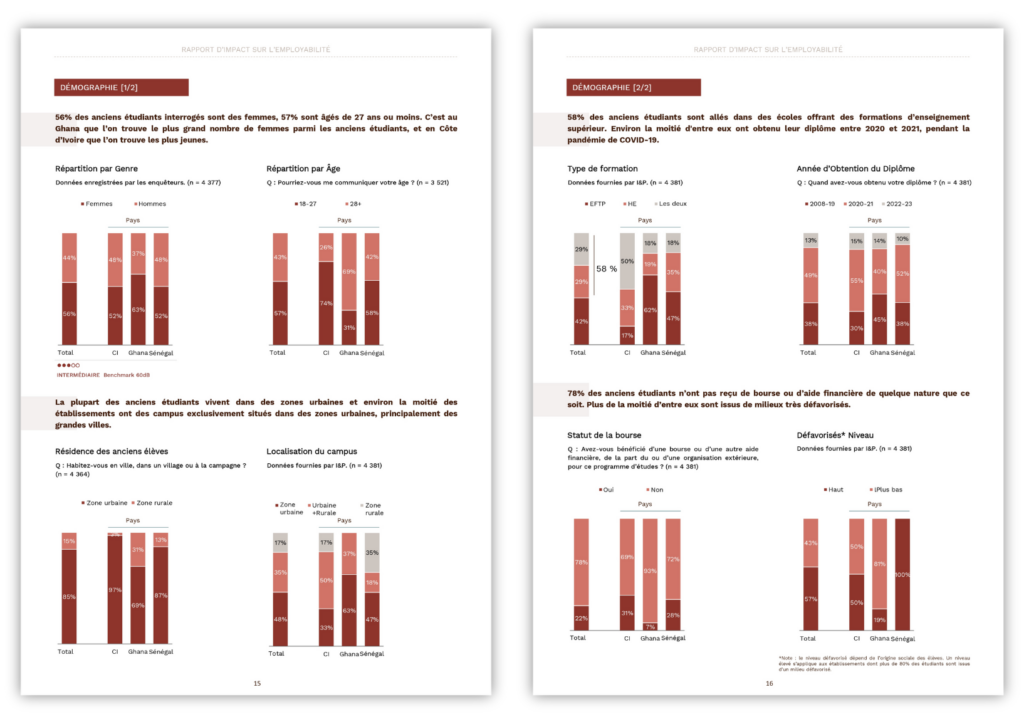
The current dynamics of the African population is unique and will inevitably have a significant influence on the global demographics of the 21st century, and on the development of the continent. Will Africa follow the lead of Asian countries, whose economic growth was largely due to a particularly high demographic dividend? The potential is immense, but the path(s) to achieve it are still uncertain…
An unprecedented population growth
Africa’s population more than tripled in the second half of the 20th century, from 230 to more than 800 million people today. In 2004, the United Nations projected the African population at 2.2 billion by 2100. Less than two decades later, Africa’s demographic trajectory has surprised everyone, including demographers, making these forecasts completely obsolete. The reason is simple: fertility has not declined as expected. The African continent has not followed the trajectory of Asia or Latin America, where the number of children per woman has fallen from an average of 5 to 2.5 between 1970 and today.
According to the most recent forecasts, it is as early as 2050 that the African population will exceed 2 billion people (reaching 2.4 billion to be more precise). This represents more than 42 million additional people each year by 2050, 3.5 million people more per month or 80 per minute. That’s the equivalent of the population of Dakar every month! By the end of the century, the continent will contribute 82% of the total population growth, representing 3.2 billion people out of a total of 3.8 billion.
The changes at work in African demographics are relatively simple. Indeed, since the mid-20th century, public health has improved, leading to both a sharp drop in infant mortality and an increase in life expectancy[1]. At the same time, the average number of children per woman (the total fertility rate) remains the highest in the world. As a result, the continent has the youngest population on the planet, with more than 40% of Africans under 15 years of age.
This demographic boom, with a birth rate four times higher than mortality, may generate concern and uncertainty, especially if poorly managed. However, it should be remembered that population growth is not necessarily a disabling factor in itself, it is even desirable and sought after from an economic point of view.
The demographic dividend, a development opportunity…
The continent has not yet achieved the (much awaited) demographic transition, the key to the demographic dividend. This term refers to the economic benefit resulting from a significant increase in the ratio of working-age adults to dependants (children and the elderly). When birth rates fall sharply, the age structure changes in favour of a larger number of working-age adults. The corollary of this process is an acceleration of the economic growth through increased productivity, higher savings for households and a reduction of the cost of basic social services.
If this transition attracts so much attention, it is because economists and development actors have in mind the economic take-off model of the Asian Tigers and Dragons. In a quasi-consensual way, economists identify as a major basis for this economic take-off the achievement of a particularly high demographic dividend, which has ultimately made it possible to reduce poverty and inequality. However, the benefits of this dividend were made possible by significant upstream preparation: substantial investments in physical capital, particularly human capital, strong savings, sound management of the economy, a development policy geared towards exporting industries, etc.
In terms of its demographic dividend, the African continent seems to be following a slightly different trajectory. However, in the light of the Asian experience, what are the current African investment priorities to realize the full potential of the demographic dividend?
Africa facing its possible demographic dividend
If we take the case of Europe, the demographic transition occurred more than a century ago. During this period, the population was able to adapt socially and economically in response to reduced mortality and fertility (Reher, 2011). Thus, with the decline in infant mortality, families’ investment in their children’s health and education and women’s participation in the labour market have increased. As for Asia and Latin America, they have experienced a fast transition rate due to the use of more advanced technologies such as vaccines, antibiotics and modern contraceptive methods from the beginning of their transitions. For example, it is estimated that the demographic dividend experienced by East Asian countries accounted for more than 20% of economic growth between 1960 and 1980 (Bloom and Williamson 1998, Bloom et al. 2000). This Asian demographic dividend largely explains the difference in development between many East Asian and African countries. In East Asia, the cumulative effects of a rapid decline in fertility and an increase in the labour force relative to children and dependent adults led to a recovery in economic productivity between the 1970s and 2000 (Bloom et al., 2003; Eastwood and Lipton, 2012). This has been possible above all because these countries benefited from strong political leadership and clear development plans, by investing massively in quality education and young people’s readiness for employability, Foreign Direct Investment’s attractiveness, and extending access to family planning services.
Africa could follow the same path. It is now in a historical demographic configuration that could enable it to benefit from its dividend. But this change in the age structure, as a result of the demographic transition, is a necessary but not sufficient condition for achieving the demographic dividend. Thus, it is crucial to make prior investments in education, health, family planning, urbanization, and the private sector, especially SMEs and governance. These investments must be made before the transition to an economically favourable age structure in order to benefit from the demographic dividend. These factors help to explain, for example, why Niger’s population is growing at a rate of 3% per year, while Botswana’s is growing at a rate of 1% per year. At the same time, the continent is threatened by a relatively short period of anticipated investment in these countries. This could prevent these important demographic changes from being fully exploited in a stable and sustainable manner (Reher 2011). These priority reforms and investments are already beginning to resemble emergencies.
The challenges of fertility and family planning
The control of African demography is still lacking financial and human resources due to weak political commitment, lack of data and insufficient research in this field. Furthermore, fertility and family planning issues have rarely been given priority in the past 30 years, coming second only to major public health emergencies: HIV/AIDS prevention, pregnancy management, obstetric and neonatal interventions, cholera and Ebola epidemics, etc.
As a result, many Sub-Saharan African countries are still in the early stages of their demographic transition. Yet, in order to achieve sustained and sustainable growth that improves people’s well-being, it is essential to reduce fertility levels[2] today in order to accelerate demographic transition and reduce the dependency ratio. This transition is slower than in other developing regions. Although economic growth rates have been rapid and robust in recent decades, fertility levels continue to create a risk of unpredictability in the continent’s long-term development dynamics. This fertility decline is a complex process that can only be made possible at the family level through women’s access to information and voluntary use of modern contraceptive methods to meet their family planning needs. The information component is therefore an essential part of the process. About 25% of women in developing countries have unmet family planning needs, i.e. they want to avoid pregnancy, but do not have access to or use modern contraceptive methods (Darroch et al 2011, WHO and UNICEF, 2012). It should also be noted that the choice of spacing or limiting births depends directly on several factors, including the health and survival of existing children, knowledge of the health benefits of spacing births, the value of investing in the education of existing children, the opportunity cost for women to have additional children, etc.
Policies and programmes in the health and education sectors should be strengthened to help reduce the target size of the family. For the level of women’s education, their participation in the formal labour market and children’s health are negatively correlated with the desired fertility level. In addition, limited access to appropriate facilities and modern contraceptive methods, as well as the sometimes poor quality of counselling, are largely responsible for the failures observed (WHO, 2015). This reflects a real need to improve access and quality of family planning facilities in an effort to increase the voluntary use of modern contraceptive methods, which will lead to a more rapid decline in fertility in all countries. In West Africa, for example, there is always one inactive person for every working person, i.e. the dependency ratio is 100%. An increase from 4 to 5 times the current resources dedicated to family planning would allow countries to halve their level of dependency in twenty years’ time (Guengant, 2015).
Employment, a key issue
Sub-Saharan Africa has the youngest population in the world. The under-25s represent 67% of the population and the 15-24 age group alone represents 1/5 of the world’s youth population. More and more of them are migrating to urban areas due to deteriorating living conditions in rural areas (World Bank, 2015). But no matter where they come from or where they go, this young population has high expectations. Despite many efforts, job creation, especially for young people, in most African countries remains totally disconnected from population growth. And while this labour force is the continent’s most important competitive advantage, unfortunately three out of five of the unemployed are young people (ILO, 2017). Even the most skilled young people find themselves in low-paying jobs…when they can find them. This high level of unemployment represents a real shortfall and severely limits the potential for a demographic dividend. Worse still, this youth could represent a real threat to the stability of the continent because under-educated and unemployed young people are more exposed to illegal activities and in the grip of armed conflict and terrorism. This structural unemployment of young people is largely due to a mismatch between training, skills offered and employer requirements, a predominantly informal and insufficiently promoted entrepreneurship, a significant digital and technological divide, acute difficulties in accessing capital and the scourge of corruption.
Decision-makers must define educational programmes in the light of today’s and tomorrow’s jobs, in close consultation with private sector actors. In this respect, it is essential that school and academic training be rethought if we are to produce skills that meet employers’ expectations. This goes hand in hand with the integration of low-skilled young people into professional programmes. For most graduates, obtaining their first work experience is the most difficult step. To remedy this, incentives could be provided to companies that encourage, for example, internships, apprenticeships, etc.
Entrepreneurship is also a way forward. Historically, African states have considered entrepreneurship and innovation as a marginal component of the economy, as evidenced by the absence of a dedicated ministry in most countries. Obviously, in a context of scarce formal employment, coupled with a rapidly growing population of young people, the latter are more encouraged or even forced to show entrepreneurial ingenuity to earn a living. They are everywhere in African cities, trying to sell everything from phone cards to tissues, water bottles and handcraft products. Inside each neighbourhood, women run sewing or hairdressing workshops… while young men wash vehicles, carve wood or repair flat tires. In lively markets, they sell locally grown fruits and vegetables, imported second-hand clothing, mobile phones or household products. On the main arteries of cities or in the hinterland, they fill potholes on the roads or regulate traffic in exchange for a possible financial generosity from motorists. Although this entrepreneurship is very small and largely informal, it is the primary source of livelihood for young Africans (Welter, 2017). In this respect, the entrepreneurial question must be at the heart of public policy making. This includes a favourable regulatory framework and a simplification of business creation, a facilitated access to finance, the creation of incubators and accelerators, the allocation of investment grants, the promotion of entrepreneurship and initiative spirit, the support to research institutes, etc. It should be noted that these initiatives may not be effective if they are implemented in an uncoordinated and isolated manner.
It should also be noted that agriculture and SMEs are central to this reflection. The agricultural sector is the main source of employment on the continent (60% of the working population) and has the extraordinary potential to be a viable investment sector for young people if it is made attractive. This sector could thus make its transition from subsistence to commercial agriculture. As for SMEs, they constitute the backbone of African economies with nearly 90% of the entrepreneurial fabric and about 80% of jobs. The success of these companies is a prerequisite for the employment of young people. But they remain chronically confronted with a credit rationing that limits their growth and generally leads to dead-end entrepreneurial adventures. Consequently, conditions must be created to diversify financing options. These options are many and varied: microfinance, business angels, traditional bank loans, leasing, capital investment and in particular impact investment that prioritizes companies with high social and environmental added value, crowdfunding, equity loans, etc.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that today Africa is at a crucial turning point to benefit from the full potential of its demographic dividend. We are almost at the critical moment, when the working-age population will be at its peak. For the African continent to benefit from this demographic dividend, the measures to be implemented as a matter of priority (or even urgency) are numerous, in order to have a well-trained and healthy working age population in the medium term:
• The creation of a political and economic environment conducive to long-term investment
• Young people must be at the heart of public policy and development strategies
• Investments in education, health, family planning, women’s empowerment, skills development, innovation
• Facilitating access to finance, promoting youth employment, supporting the private sector in particular, entrepreneurship and the fabric of SMEs
The size of the dividend will depend on the pace of the demographic transition and public policies. It cannot be total and live up to expectations unless these reforms and prior investments are made. This is a duty of lucidity that seems essential if the African continent is to meet the aspirations of its young population and ensure its demographic dividend.
Notes
[1] The 12 million Africans born in 1955 could only hope to live to 37 years old, while the 30 million Africans born last year can hope to live to over 60 years old.
[2] The fertility level remains the highest in the world, with an average of more than 5 children per woman (UN population).