Since the 2000s, there has been a massive expansion in private higher education provision. This offer is characterized by diversity, ranging from micro-institutions with few resources to large university groups….
Since the 2000s, there has been a massive expansion in private higher education provision. This offer is characterized by diversity, ranging from micro-institutions with few resources to large university groups. This rapid growth reinforces the need to measure the social impact of these institutions, in order to guarantee and control the quality of the training on offer.
In partnership with 60_decibels (1), an impact measurement company, I&P Education to Employement (2), a funding program that aims to improve access to quality education, has set up “lean data” surveys to monitor and improve the measurement of the impact of companies funded by the program.
Between 2021 and 2023, 60dB conducted 23 studies with 18 post-secondary institutions. Researchers trained by 60dB conducted 5,448 telephone interviews with alumni of the institutions. These alumni were randomly selected from databases compiled and shared by each institution, with cohorts ranging from 5 years up to their entry into the IP2E program. Where possible, 60dB targeted a sample of 200-250 alumni per institution, to guarantee a 90% confidence level and a 5% margin of error. These data were essential to help companies better understand their role in their alumni’s career paths. They guided the implementation of strategies, supported by IP2E, to improve their impact on their current students.
In a subregional context of data scarcity, this article looks at the main indicators that educational companies should take into account when measuring their impact.
To access the full report : click here
- Understanding the demographic profile of your students
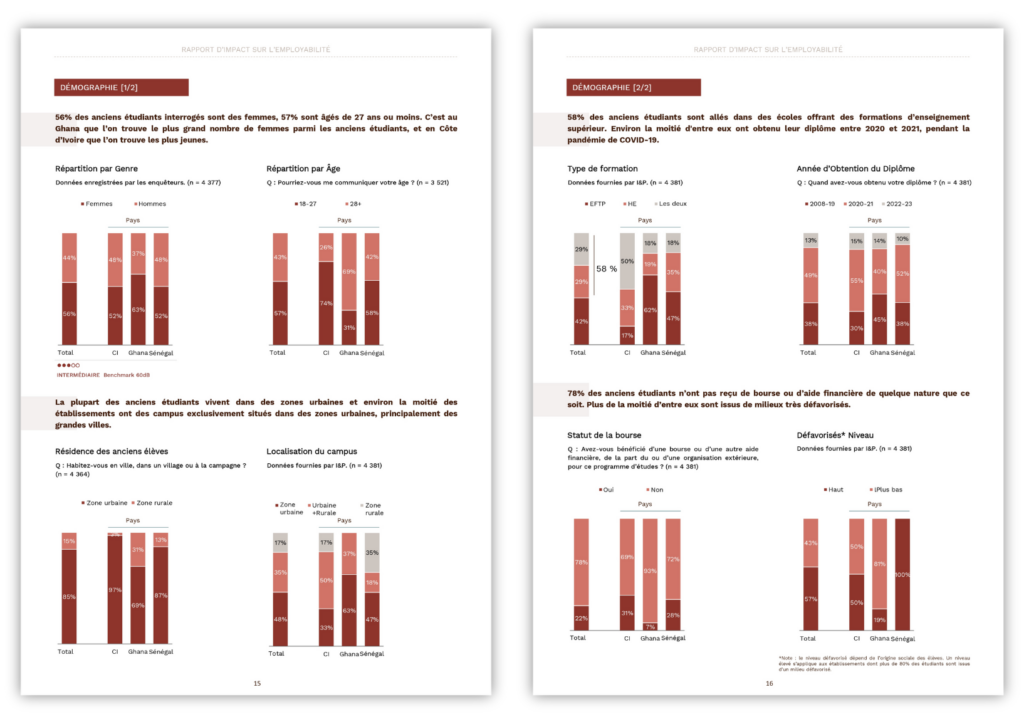
Institutions need to understand not only the geographical, but also the socio-economic origins of their students. These segmentations are essential, in order to assess whether all students, whatever their gender, age, socio-economic level or place of residence, have the same chances of finding a job. These parameters can guide companies in setting up specific mechanisms, such as social grants, or relocation to rural areas.
I&P, through the IP2E program, investigates whether students come from disadvantaged backgrounds, by examining key variables: whether they live in rural areas, whether they study in areas where socio-economic development indicators are low, and whether they need social inclusion mechanisms (i.e. scholarships) to pursue their studies. For the purposes of this report, institutions with more than 80% of students from disadvantaged backgrounds are classified as having a “high” level of disadvantage.
- Measuring professional integration
The professional integration of graduates is a key indicator of the effectiveness of educational institutions, but its measurement is complex.
For the purposes of this study, the insertion rate refers to the proportion of former students who report being currently employed, and who report having found a job within six months of graduation. Graduates’ insertion rates can be influenced by external factors such as economic conditions, making it difficult to attribute employment directly to the quality of the education received.
At the time of the study, 61% of alumni from IP2E portfolio institutions were employed. 39% found a job within six months of their training.
Institutions also need to understand the reasons why their alumni are not employed. Alumni interviewed cited a lack of job opportunities in a competitive environment, administrative problems with their institutions and career transitions to explain this situation. 10% were still studying at the time of the study.
- Identifying the most promising career paths
The study revealed that former students with a vocational training diploma are more likely to enter the job market independently, and therefore have the highest average integration rate, at 46%. Institutions also need to determine whether the skills imparted are being used by students in their work.
- Knowing how to find a job
Establishments can measure their contribution to students’ job search. To do this, they need to identify through which intermediaries students have found their jobs. In our study, nearly 3 out of 10 former students relied on friends or family to find a job. 15% also rely on external networks. Only 12% find their jobs through the career guidance services offered by the schools. Yet this is one of the main reasons why students recommend their school. Companies therefore need to strengthen their career services.
- Find out about graduated satisfaction
Alumni’s employment status influences their level of satisfaction with the school. The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a common indicator of customer satisfaction and loyalty. The study reveals that it is higher among employed students than among unemployed ones. Former students take into account the quality of training, the relevance of training, the learning environment and the support given to students in their job search.
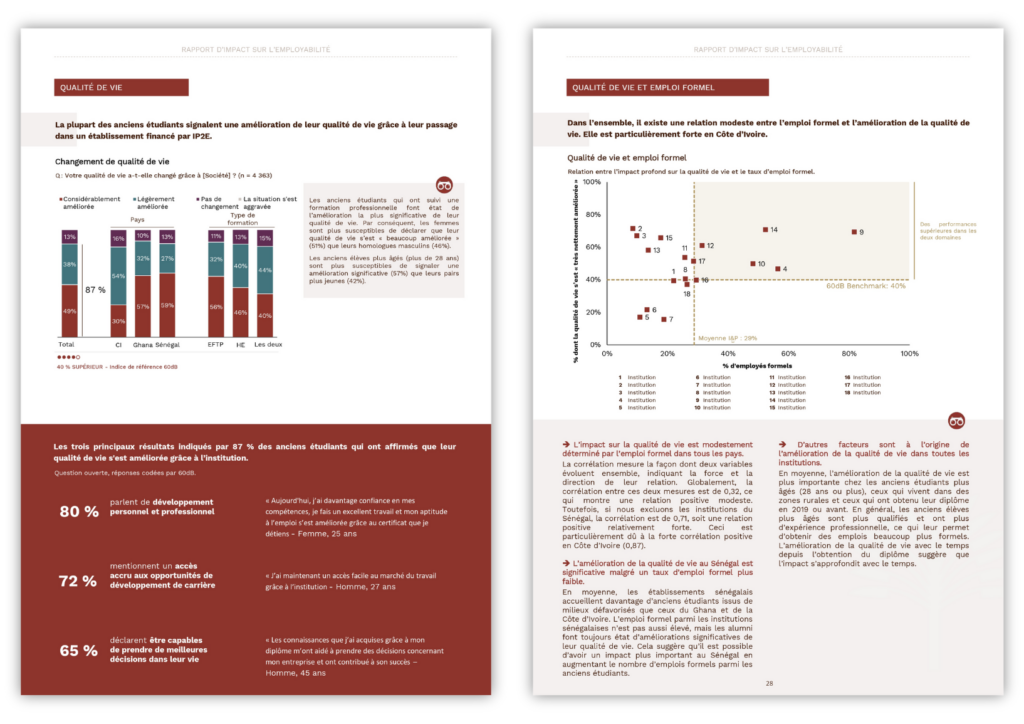
- Integrating the multi-dimensionality of impact measurement
60 dB has created an impact index specific to I&P: the I&P Education Impact, which includes the factors most cited by alumni in defining their quality of life. It was measured through a deliberately open-ended question, to find out how alumni perceive their well-being. The most important parameters that emerged were :
-
-
- Employment conditions: the most fundamental factor is having a job, whether formally or informally, or through self-employment or an advisory role.
- First job: getting your first job within six months of graduating is also a key factor in effective professional integration.
- Retirement benefits: the retirement pension is the first social benefit declared and serves as an indicator of formal employment. It is a sign of access to a basic and essential benefit.
- Job satisfaction: the type of job (formal, informal, internship, self-employment) also plays a key role.
- Satisfaction with salary: similarly, in addition to satisfaction with the job itself, satisfaction with salary is also important, as it covers the financial aspects.
- Quality of Life: the improvement in general well-being, as perceived by alumni themselves, is a key impact indicator.
-
By 2030, 30 million young people will be entering the African job market every year. Universities and vocational training centers play a vital role in enabling students to develop their skills to the full and make an effective contribution to the job market. The impact of higher education institutions in West Africa is multidimensional, encompassing professional insertion, social inclusion and improved quality of life for students. Measuring this impact presents significant but essential challenges for informing educational policies and institutional practices.
(1) 60_decibels is an impact measurement company that brings speed and scalability to social impact measurement and customer insight.
(2) The I&P Education to Employment Initiative (IP2E), an impact financing program launched in 2021 that aims to improve access to quality education and strengthen the training-employment match in Africa, in order to guarantee better employment opportunities. IP2E finances and supports private companies in the post-secondary education ecosystem.